1. Image Recognition
|
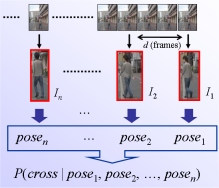
Recognition of Pedestrian's Intent We propose a method for estimating the crossing intention of a pedestrian on a sidewalk from the pedestrian's posture and change in posture in multiple frames during a short period of video images. R. Furuhashi, K. Yamada, "Estimation of Street Crossing Intention from a Pedestrian's Posture on a Sidewalk Using Multiple Image Frames," Proc. 2011 First Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition (ACPR2011), pp. 17-21, Nov. 28-30, 2011. |

|
Detection of Unusual Human Behavior This project aims to detect unusual human behavior from video images for automated visual surveillance by learning examples of usual behavior. Histogram of oriented gradients of Motion History Image is used for describing the features of human movements. H. Murayama, K. Yamada, "Detection of Unusual Human Activity based on Sequence of Actions with MHI and CDP," Proc. of the 2010 IEEE Region 10 Conference (TENCON2010), pp. 1663-1667, Nov. 21-24, 2010. |
|
Detecting Unusual Objects in a Scene The aim of this research is to detect abnormal objects in a road scene based on local features by supposing that an abnormal object is an object that does not appear in usual scenes. J. Kobayashi, K. Yamada, "Detection of Abnormal Objects in a Scene based on Local Features," Proc. of IAPR Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA2009), pp. 34-37, May 2009. |
|
Detecting the Change in Human Condition from Facial Expression Monitoring human condition on the basis of facial expression with a video camera. Detects unusual facial expression from input images with a classifier trained with facial images of usual facial expressions. K. Suzuki, T. Takeshima, J. Kobayashi, K. Yamada, "Detection of unusual facial expression for human support systems," Proc. of IEEE IECON'08, pp. 3414-3418, 2008. |
2. Driver Behavior Recognition
|
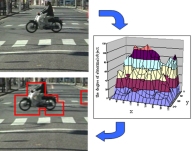
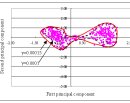
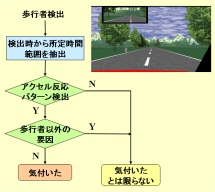
Estimating Driver Awareness of Pedestrians We proposes a new approach for estimating the awareness a driver has of pedestrians appearing on the road ahead. The proposed method estimates the probability of the driver being aware of the pedestrian from the observation of driver's acceleration reaction. Yuuki Fukagawa, Keiichi Yamada, "Estimating Driver Awareness of Pedestrians from Driving Behavior Based on a Probabilistic Model," 2013 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, pp. 1155-1160, June 23-26, 2013. |
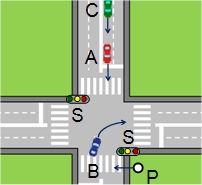
|
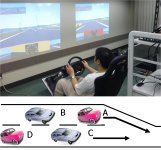
Driver-Intent Estimation at Yellow Traffic Signal Predicts whether a driver approaching a signalized intersection decides to stop or pass through the intersection when the traffic signal turns yellow from green based on the situation and the vehicle behavior. R. Mabuchi, K. Yamada, "Study on Driver-Intent Estimation at Yellow Traffic Signal by Using Driving Simulator," Proc. 2011 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV 2011), pp. 95-100, June 2011. |

|
Predicting Unusual Right-turn Driving Behavior at Intersection Unusual driving behavior could be a sign of human error that increases the risk of accidents. We propose a method for predicting the possibility a driving behavior leads to an accident from the information on the vehicle behavior and the situation. T. Hayashi, K. Yamada, "Predicting Unusual Right-turn Driving Behavior at Intersection," Proc. of 2009 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV2009), pp. 869-874, June 3-5, 2009. |
|
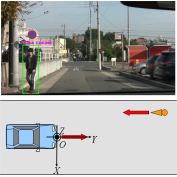
Detection of Unusual Pedestrian Behavior A new approach for predicting the possibility of a collision between a vehicle and a pedestrian is proposed. Pedestrian behavior that deviates from usual pedestrian behavior indicates a possibility where the vehicle must take urgent evasive action to avoid collision with the pedestrian. From such a viewpoint, we propose a method for predicting whether the pedestrian behavior deviates from usual pedestrian behavior. K. Nakatsubo, K. Yamada, "Detecting Unusual Pedestrian Behavior toward Own Vehicle for Vehicle-to-Pedestrian Collision Avoidance," Proc. of 2010 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV2010), pp. 401-405, June 2010. |
|
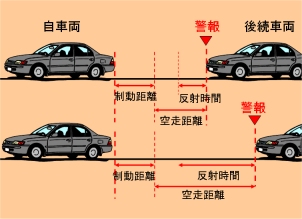
Driving Support System Adaptive to the State of Surrounding Vehicle Drivers A concept of a driving support system that is adaptive to the state of surrounding vehicle drivers is proposed. The effectiveness of the concept is shown by a simulation study for a case that the driver support system is a rear-end pre-crash safety system and the state of surrounding vehicle drivers is the expected reaction time of the following vehicle driver. H. Fukuoka, Y. Shirai, K. Yamada, "Driving Support System Adaptive to the State of Surrounding Vehicle Drivers," Proc. of 2009 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV2009), pp. 1215-1220, June 3-5, 2009. |
|
Interaction of Driving Behavior between Drivers Estimation of driver intention is a key technology in the advancement of driver assistance systems. Previous studies in regard to driver intention estimation primarily involve situations where there is no great deal of mutual interaction between the drivers. In contrast, this study looks at situations where there is a strong mutual interaction between drivers. This reseach addresses the problem of the driver intention estimation in this type of situation by proposing a novel approach to analyze the interaction of driver intent through the vehicle behavior. K. Yamada, H. Matsuyama and K. Uchida, "A Method for Analyzing Interaction of Driver Intention through Vehicle Behavior When Merging," 2014 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV2014), pp. 158-163, June 8-11, 2014. |
